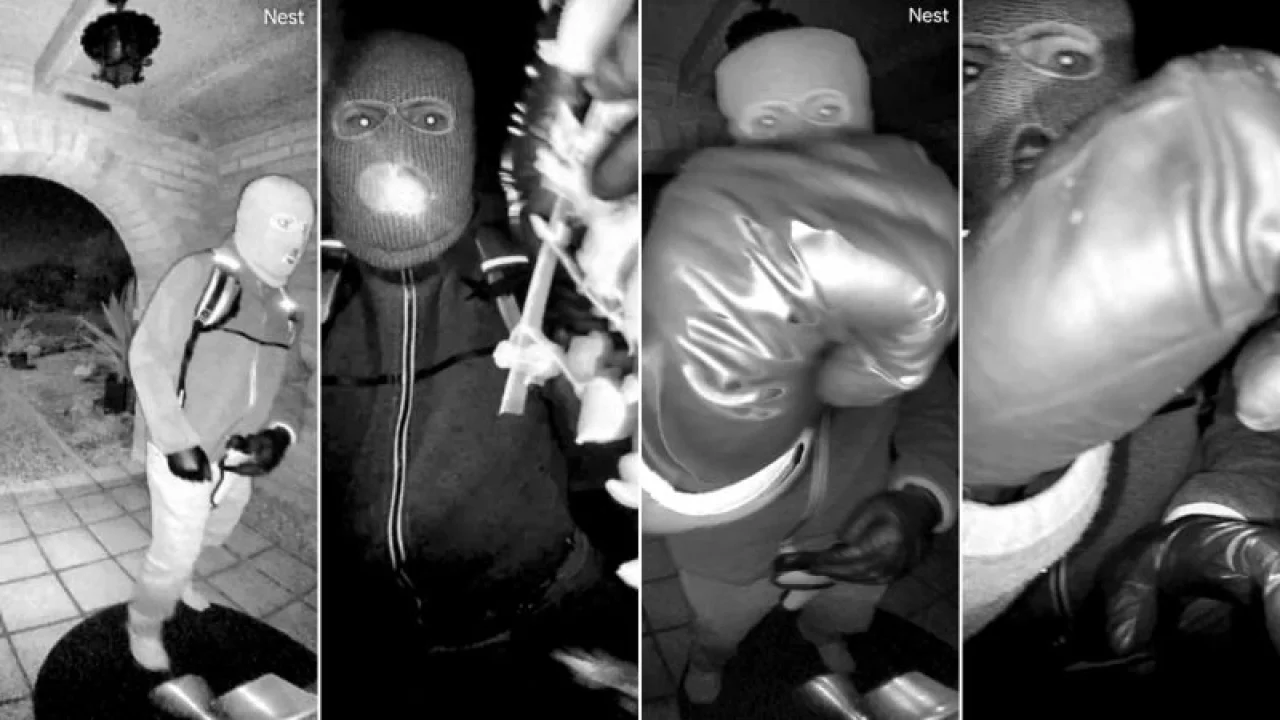

Imagine frantically checking your home security cameras after a break-in, only to discover your subscription had lapsed and all the footage was supposedly gone forever. That sinking feeling of helplessness hits hard—until someone tells you the video might still be recoverable somewhere in the digital maze of cloud servers.

This exact scenario played out on a much larger scale in Arizona, where the disappearance of Nancy Guthrie, mother of “Today” show host Savannah Guthrie, initially seemed to leave investigators without crucial video evidence. What happened next showcases how Google nest video recovery became the key to unlocking vital clues in a missing person case that captivated the nation.
The breakthrough came after days of technical detective work that even seasoned investigators weren’t sure would succeed.
When “Deleted” Data Isn’t Really Gone
The Nancy Guthrie case took a dramatic turn when authorities initially announced there was no video available from her Nest security cameras. Pima County Sheriff Chris Nanos explained that Guthrie had no subscription to Google’s cloud recording service, which typically keeps videos accessible for extended periods.
But here’s where the story gets interesting—and offers hope to anyone who’s ever lost important digital files. Even without a paid subscription, Nest cameras still capture about three hours of “event-based” video before it gets deleted from Google’s systems.

The problem? By the time investigators knew to look for it, that three-hour window had long passed. Or so they thought.
Google engineers stepped in to attempt what seemed impossible: recovering video data from their vast network of servers and backup systems. The task was so technically complex that even FBI investigators weren’t certain it would work.
“A delete function is just telling the file system to ignore that data and feel free to use that space on the hard drive for new data,” explains Nick Barreiro, an audio-video forensic analyst. “Until it’s actually used again, that old data is still recoverable.”
The Technical Miracle Behind Video Recovery
Understanding how Google nest video recovery works requires diving into the complex world of cloud computing. When your Nest camera records a video, that footage doesn’t just sit in one place—it travels through what experts call “layers and layers” of digital components.
Here’s what happens to your video data in Google’s system:
- Initial capture and compression at the camera level
- Upload to Google’s cloud servers for processing
- Conversion into different formats for viewing
- Distribution across multiple backup servers worldwide
- Temporary storage in various processing queues
- Final deletion from active systems
| Recovery Method | Success Rate | Time Frame |
|---|---|---|
| Active cloud storage | 95% | Within subscription period |
| Free event history | 85% | Up to 3 hours |
| Residual server data | 40% | Days to weeks |
| Backup system fragments | 20% | Weeks to months |
Adam Malone, a cyber crisis expert and former FBI agent, describes the process: “There might be one component that processes data into a compressed format, another that renders it visually.” Each step creates potential recovery points.
The footage and its underlying data could travel through hundreds of thousands of servers across the globe, increasing chances that fragments remain somewhere in the system even after “deletion.”
“It could be that this video was sitting in a processing queue that just hadn’t been purged yet,” Malone explains. Sometimes luck plays a role alongside technical expertise.
What This Means for Everyday Users
The successful Google nest video recovery in the Guthrie case offers both hope and important lessons for regular homeowners who rely on security cameras.
First, the good news: your “deleted” footage might not be as gone as you think. Cloud-based systems like Nest create multiple copies and fragments of data as part of their normal operations. This redundancy, designed for reliability, can become a lifeline when you need to recover important footage.
However, there are realistic limitations to consider. Google’s intervention in the Guthrie case involved FBI search warrants and the full technical resources of one of the world’s largest tech companies. Regular consumers can’t expect the same level of recovery assistance for typical situations.
The case also highlights why paying for extended cloud storage makes sense if you’re serious about home security. While free services provide basic coverage, subscription plans ensure your footage remains accessible for weeks or months rather than hours.
“I’ve had cases where I could go back months or even years and find fragments of video files still on hard drives,” Barreiro notes. But accessing this data typically requires professional forensic services and legal authority.
For most homeowners, the key takeaway is understanding your camera’s storage settings before you need the footage. Know how long your videos are kept, whether you’re paying for extended storage, and what happens when that storage period expires.
The technology that made this recovery possible exists because modern cloud systems prioritize data preservation and redundancy. Your video doesn’t just vanish the moment it’s “deleted”—it often remains scattered across multiple servers until new data overwrites those specific storage locations.
This case demonstrates that even when traditional recovery methods fail, innovative technical solutions might still exist. The collaboration between law enforcement and private companies like Google creates possibilities that didn’t exist even a few years ago.
While we can’t all expect Google engineers to personally recover our lost vacation videos, understanding how these systems work helps us make better decisions about digital storage and backup strategies. The Nancy Guthrie case proves that in our interconnected digital world, “permanently deleted” sometimes isn’t as permanent as we think.
FAQs
Can Google recover deleted Nest camera footage for regular users?
Google typically only performs complex data recovery for law enforcement investigations with proper legal warrants, not for individual consumer requests.
How long does Nest keep free video footage?
Nest cameras save approximately three hours of event-based video history for free users before automatic deletion occurs.
What increases the chances of recovering deleted security footage?
Acting quickly, having paid cloud storage, and understanding that data might exist in backup systems or processing queues even after apparent deletion.
Do other security camera brands offer similar recovery possibilities?
Most cloud-based security systems have similar data architectures, meaning recovery might be possible, but each company has different policies and technical capabilities.
Should I pay for extended cloud storage on my security cameras?
If you rely on cameras for actual security rather than casual monitoring, paid storage plans provide much better protection and longer retention periods.
How do investigators typically request video data from tech companies?
Law enforcement must obtain proper search warrants or subpoenas to request data from companies like Google, following established legal procedures for digital evidence.