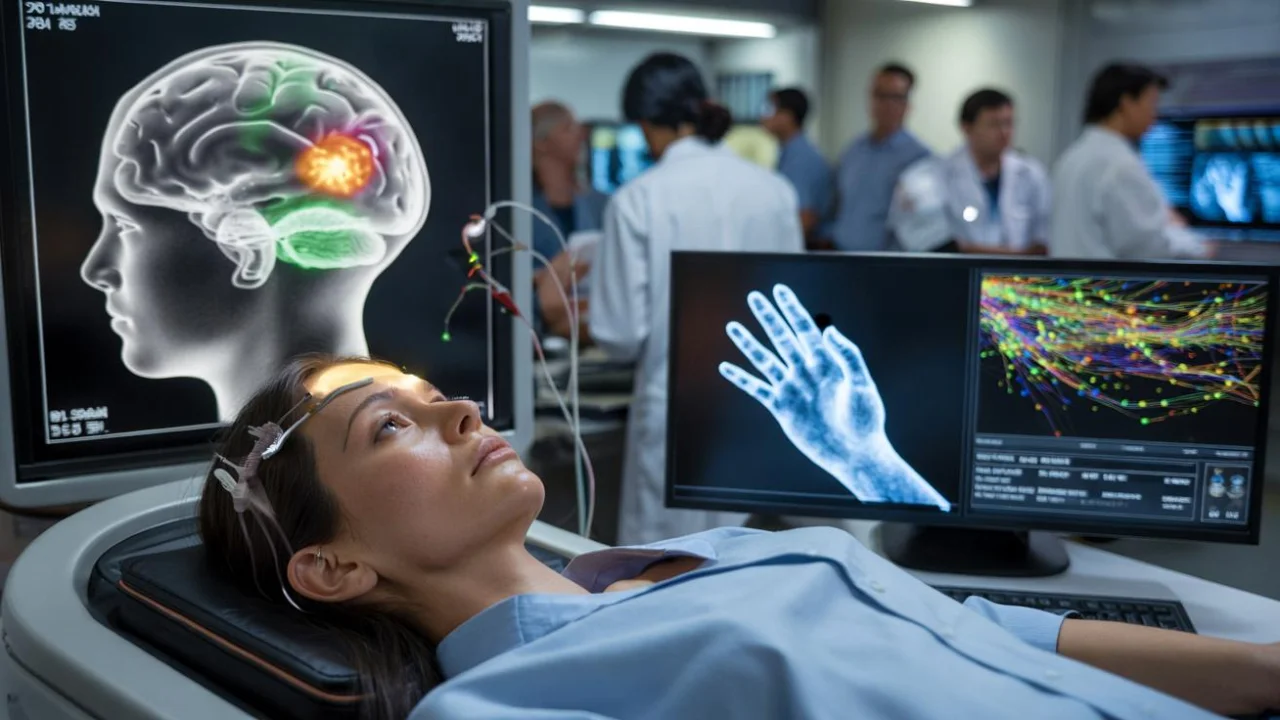
Sarah sits in her therapist’s office, describing the fog that settles over her mind every morning. Depression has stolen her ability to feel motivated, to find joy in simple things like her daughter’s laughter or a warm cup of coffee. What she doesn’t know is that three floors above her, in a research lab, scientists are learning to speak directly to the brain circuits that control exactly what she’s lost.

They’re not using scalpels or drugs. Instead, they’re teaching machines to recognize the electrical whispers of specific thoughts and emotions, then gently steering those same circuits back toward balance. It sounds like science fiction, but it’s happening right now in labs around the world.
This breakthrough represents something unprecedented: machine learning brain circuits working together to potentially treat conditions that have puzzled doctors for centuries. We’re watching the birth of precision neuroscience.

How Machines Learn to Read Your Mind
Picture your brain as a bustling city at night, viewed from an airplane. Each light represents a neuron firing, and clusters of lights show neighborhoods of brain cells working together. For decades, scientists could only watch these patterns and guess what they meant.
Now machine learning algorithms are cracking the code. They analyze thousands of neural recordings, learning to recognize the unique electrical signatures of specific thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. It’s like teaching a computer to read the brain’s own language.

“We used to think we needed to understand everything about the brain before we could help it,” explains Dr. Maria Rodriguez, a computational neuroscientist at Stanford. “Machine learning showed us we could help first and understand later.”
The technology works by monitoring brain activity through various methods – from external electrodes to tiny implanted sensors. As the algorithms watch, they begin to notice patterns invisible to human researchers. They learn that when you feel anxious, certain circuits light up in a specific sequence. When you’re motivated, different pathways activate.

But here’s where it gets really interesting: once the machine learning system understands these patterns, it can work backward. Instead of just watching brain circuits fire, it can stimulate them with precisely targeted electrical pulses, magnetic fields, or even light.
The Science Behind Precise Brain Control
The technology behind machine learning brain circuits involves several sophisticated approaches that work together to create unprecedented precision in neuroscience:

- Real-time pattern recognition: AI algorithms analyze brain signals thousands of times per second, identifying specific neural signatures
- Targeted stimulation: Once patterns are recognized, the system delivers precise stimulation to specific brain regions
- Feedback loops: The technology continuously monitors results and adjusts its approach in real-time
- Multi-modal sensing: Advanced systems combine multiple types of brain monitoring for comprehensive circuit mapping
Research teams have achieved remarkable results across different applications. At MIT, scientists trained algorithms to identify the exact neurons responsible for specific memories in mice, then used light to turn those memories on and off like switches.
Meanwhile, researchers at the University of Washington developed a system that can predict and prevent seizures by recognizing the electrical patterns that precede them, then delivering targeted stimulation to interrupt the process.
| Research Institution | Focus Area | Key Achievement | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stanford University | Depression Treatment | 70% response rate in treatment-resistant patients | 2023 |
| MIT | Memory Control | Selective memory activation in animal models | 2024 |
| University of Washington | Seizure Prevention | 85% reduction in seizure frequency | 2023 |
| UC San Francisco | Paralysis Recovery | Restoration of hand movement in paralyzed patients | 2024 |
“The precision we’re achieving would have been impossible just five years ago,” notes Dr. James Chen, who leads a neural engineering lab at Johns Hopkins. “We’re not just stimulating the brain anymore – we’re having conversations with it.”
Real People, Real Changes
The impact of machine learning brain circuits extends far beyond laboratory experiments. Real patients are already experiencing life-changing results from these technologies.
Take Marcus, a 34-year-old veteran who lost his ability to move his hands after a spinal cord injury. Traditional treatments offered little hope. But researchers at UC San Francisco implanted tiny sensors in his motor cortex and connected them to a machine learning system.
The AI learned to interpret the signals Marcus’s brain still sends when he thinks about moving his hands. Within weeks, those thoughts were controlling a robotic hand with remarkable precision. He can now pick up a coffee cup, write with a pen, and even play simple video games.
“It’s not just about the movement,” Marcus explains. “It’s about feeling human again, feeling like my thoughts matter.”
Similar breakthroughs are transforming mental health treatment. At Stanford, researchers developed a system that can identify the specific brain circuits involved in an individual’s depression, then deliver personalized stimulation to restore normal function.
Traditional antidepressants work for about 60% of patients and take weeks to show effects. The machine learning approach is showing response rates above 70% with improvements visible in days rather than months.
The technology is also revolutionizing treatment for conditions like:
- Parkinson’s disease, with AI-guided deep brain stimulation reducing tremors by up to 90%
- Chronic pain, where machine learning identifies and disrupts pain circuits with surgical precision
- ADHD, using real-time neurofeedback to train attention circuits
- Epilepsy, with predictive algorithms preventing seizures before they begin
“We’re moving from one-size-fits-all treatments to truly personalized brain medicine,” says Dr. Sarah Kim, a neuropsychiatrist at UCLA. “The machine learning system learns each patient’s unique neural patterns and adapts accordingly.”
But the technology raises important questions. How do we ensure these powerful tools are used ethically? What happens if someone gains unauthorized access to brain control systems? These concerns are driving new research into cybersecurity for neural devices.
Despite the challenges, researchers remain optimistic. Clinical trials are expanding, and the technology is becoming more sophisticated every month. What seemed impossible just a decade ago – machines that can read and influence our thoughts – is becoming a reality that could help millions of people reclaim their lives.
The woman in Sarah’s therapist’s office may not know it yet, but help might be closer than she thinks. In labs around the world, machines are learning the language of the human brain, one circuit at a time.
FAQs
How safe is machine learning brain control technology?
Current systems undergo rigorous safety testing and are designed with multiple fail-safes, though long-term effects are still being studied.
Can machine learning read all of my thoughts?
No, current technology can only detect specific, trained patterns and cannot access complex thoughts or memories without explicit programming.
When will this technology be widely available?
Some applications are already in clinical trials, with broader availability expected within the next 5-10 years for specific conditions.
Does brain stimulation hurt?
Most patients report feeling little to no discomfort, with some describing a slight tingling sensation during treatment.
Could this technology be hacked?
Researchers are developing advanced cybersecurity measures specifically for neural devices, including encrypted communication and biometric authentication.
How much does treatment cost?
Costs vary widely depending on the condition and approach, but many treatments are becoming eligible for insurance coverage as they prove effective.